Climate change has caused Switzerland’s glaciers to develop collapsing holes, resembling Swiss cheese.
In May 2025, an avalanche from Birch Glacier submerged parts of the valley village of Blatten.
The incident reflects growing glacial instability and the urgent threat of climate-driven disasters.
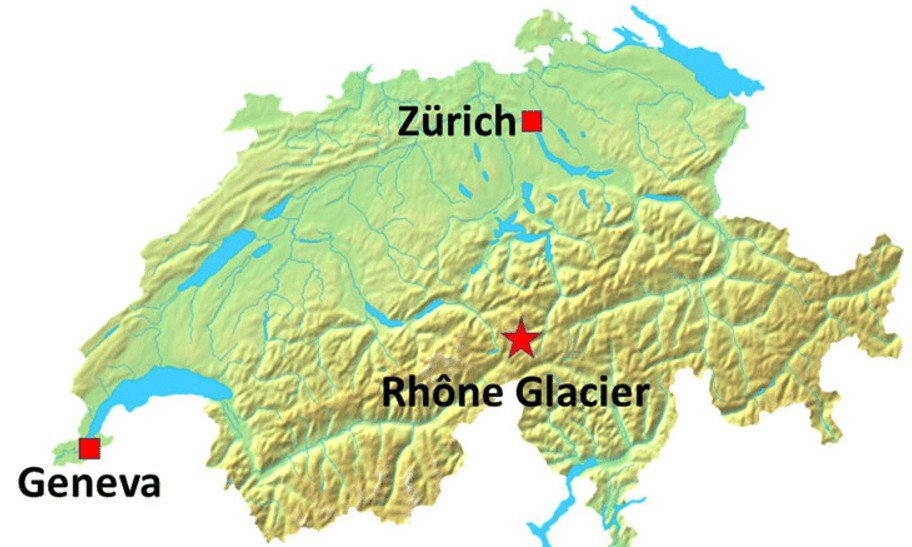
Rhône Glacier is located in the southern Swiss Alps, near the Furka Pass and the Italian border.
It is the source of the Rhône River, which flows through Switzerland and France into the Mediterranean Sea.
The Rhône River is one of Western Europe’s major rivers, important for hydropower and navigation.
The glacier is the most accessible and among the most studied in Switzerland.
It is currently the fifth largest glacier in Switzerland and is popular for scientific tourism.
Its surface shows prominent crevasses and ice caves, revealing active glacial movement.
Glacial retreat has accelerated since the 19th century due to global warming.
Scientists predict the Rhone Glacier may completely vanish by the 21st century’s end.
The glacier is covered with UV-resistant thermal blankets to reduce ice melting during summer.
Switzerland and the Alps have lost over 60% of glacier volume in the past century.
The Swiss Alps have over 1,500 glaciers, the highest number in Europe.
The Alps are Europe’s largest fold mountain range, spanning eight countries.
Mont Blanc, the highest Alpine peak at 4,807 m, lies on the France–Italy border.
The Alpine region influences Europe’s climate, biodiversity, and river systems.
Glacial melt in the Alps threatens freshwater supply, agriculture, and hydropower potential.
The Rhone Glacier is a key indicator of climate change in high-altitude ecosystems.
रोन ग्लेशियर:-
जलवायु परिवर्तन के कारण स्विटजरलैंड के ग्लेशियरों में स्विस चीज़ जैसे ढहने वाले छेद बन गए हैं।
मई 2025 में, बर्च ग्लेशियर से हुए हिमस्खलन ने घाटी के ब्लैटन गांव के कुछ हिस्सों को जलमग्न कर दिया।
यह घटना बढ़ती हुई ग्लेशियल अस्थिरता और जलवायु-संचालित आपदाओं के तत्काल खतरे को दर्शाती है।
रोन ग्लेशियर स्विट्ज़रलैंड के दक्षिणी आल्प्स में स्थित है, जो फुर्का दर्रे और इटली सीमा के निकट है।
यह रोन नदी का मुख्य स्रोत है, जो स्विट्ज़रलैंड और फ्रांस से होकर भूमध्यसागर में गिरती है।
रोन नदी पश्चिमी यूरोप की प्रमुख नदियों में से एक है और जलविद्युत व नौवहन के लिए महत्वपूर्ण है।
यह स्विट्ज़रलैंड का सबसे सुलभ ग्लेशियर है और विज्ञान पर्यटन के लिए प्रसिद्ध है।
यह वर्तमान में स्विट्ज़रलैंड का पाँचवां सबसे बड़ा ग्लेशियर है और अध्ययन का प्रमुख केंद्र है।
इसकी सतह पर दरारें और बर्फीली गुफाएँ दिखती हैं, जो सक्रिय हिमानी गतिविधि को दर्शाती हैं।
हिमनद का पीछे हटना 19वीं सदी से तेज़ गति से हो रहा है, विशेषकर ग्लोबल वार्मिंग के कारण।
वैज्ञानिकों का अनुमान है कि रोन ग्लेशियर 21वीं सदी के अंत तक पूरी तरह से समाप्त हो सकता है।
इसे गर्मियों में बर्फ पिघलने से बचाने के लिए UV-प्रतिरोधक थर्मल चादरों से ढका जाता है।
स्विट्ज़रलैंड और आल्प्स ने पिछले 100 वर्षों में 60% हिमनद आयतन खो दिया है।
स्विस आल्प्स में 1500 से अधिक ग्लेशियर हैं, जो यूरोप में सबसे अधिक हैं।
आल्प्स पर्वत यूरोप की सबसे बड़ी वलित पर्वत श्रृंखला है, जो आठ देशों तक फैली है।
मॉन्ट ब्लांक, जो 4,807 मीटर ऊँचा है, फ्रांस–इटली सीमा पर आल्प्स का सर्वोच्च शिखर है।
आल्प्स क्षेत्र यूरोप की जलवायु, जैव विविधता, और नदी तंत्र को प्रभावित करता है।
हिमनदों का पिघलना यूरोप की जल आपूर्ति, कृषि और जलविद्युत क्षमता को खतरे में डाल रहा है।
रोन ग्लेशियर, जलवायु परिवर्तन का एक महत्वपूर्ण संकेतक बन चुका है।