Why in the News
-
Gurdwara Darbar Sahib and the Kartarpur Corridor complex in Pakistan’s Narowal district were submerged by floodwaters from the Ravi River.
-
Large-scale evacuations had to be conducted because more than 100 people were stranded.
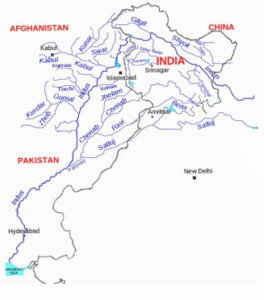
The Ravi River
Location and System
-
According to the Indus Waters Treaty (1960), India was granted access to one of the three eastern rivers in the Indus basin.
-
Before joining the Chenab River, it passes through:
-
Jammu & Kashmir
-
Punjab
-
Himachal Pradesh
-
Pakistan
-
Course and Source
-
Originates in the Chamba region of Himachal Pradesh, close to Bara Bhangal.
-
Travels via Madhopur into the Punjab plains after passing through deep gorges in Himachal Pradesh.
-
Forms a small portion of the border between India and Pakistan before crossing into Pakistan close to Narowal.
-
Flows past Shahdara (Lahore) and finally joins the Chenab near Ahmadpur Sial.
Tributaries
-
Right bank: Budhil, Baira, Siul.
-
Left bank: Ujh (J&K), Basantar, Sewa.
Key Infrastructure (India)
-
Ranjit Sagar (Thein) Dam – hydropower and irrigation.
-
Shahpur Kandi Project – downstream storage and irrigation.
-
Madhopur Headworks – off-take for Upper Bari Doab Canal (UBDC).
-
Chamera Hydropower Projects (Himachal Pradesh).
-
Proposed Ujh Multipurpose Project (J&K).
Physiography and Soil
-
Upper course: deep Himalayan gorges.
-
Lower course: fertile Doab plains of Punjab.
-
Soils:
-
Alluvial in Punjab plains
-
Savanna and ferrallitic in sub-mountain tracts
-
Climate and Hydrology
-
River fed by snowmelt and monsoon rains.
-
Seasonal floods common in Pakistan Punjab (Narowal, Shahdara, Lahore).
-
Peak flows during July–September monsoon.
Economic and Cultural Significance
-
Provides irrigation to Doab tracts of Punjab.
-
Supports hydropower generation (Chamera, Thein projects).
-
Holds religious importance – especially Kartarpur Sahib and Sikh heritage.
पोंग बांध:
क्यों समाचार में
-
पाकिस्तान के नारोवाल जिले में गुरुद्वारा दरबार साहिब और करतारपुर कॉरिडोर परिसर रावी नदी की बाढ़ से डूब गए।
-
बड़े पैमाने पर निकासी करनी पड़ी क्योंकि 100 से अधिक लोग फंसे हुए थे।
रावी नदी के बारे में
स्थान और प्रणाली
-
सिंधु जल संधि (1960) के अनुसार, भारत को सिंधु बेसिन की तीन पूर्वी नदियों में से एक तक पहुंच दी गई थी।
-
चिनाब नदी में मिलने से पहले यह बहती है:
-
जम्मू और कश्मीर
-
पंजाब
-
हिमाचल प्रदेश
-
पाकिस्तान
-
प्रवाह और उद्गम
-
हिमाचल प्रदेश के चंबा क्षेत्र में, बाड़ा भंगाल के पास से निकलती है।
-
हिमाचल प्रदेश की गहरी घाटियों से होकर गुजरने के बाद यह मधोपुर के रास्ते पंजाब के मैदानों में जाती है।
-
भारत और पाकिस्तान की सीमा का एक छोटा हिस्सा बनाती है, फिर नारोवाल के पास पाकिस्तान में प्रवेश करती है।
-
शाहदरा (लाहौर) से बहती हुई अहमदपुर सियाल के पास चिनाब में मिलती है।
सहायक नदियाँ
-
दायाँ तट: बुधिल, बैरा, सियुल।
-
बायाँ तट: उज (जम्मू-कश्मीर), बसंतर, सेवां।
प्रमुख अवसंरचना (भारत)
-
रंजीत सागर (थीन) बांध – जलविद्युत और सिंचाई।
-
शाहपुर कंडी परियोजना – डाउनस्ट्रीम भंडारण और सिंचाई।
-
मधोपुर हेडवर्क्स – अपर बारी दोआब नहर (UBDC) के लिए जल निकासी।
-
चंबा जलविद्युत परियोजनाएँ (हिमाचल प्रदेश)।
-
प्रस्तावित उज बहुउद्देशीय परियोजना (जम्मू-कश्मीर)।
भौतिक संरचना और मृदा
-
ऊपरी प्रवाह: गहरी हिमालयी घाटियाँ।
-
निचला प्रवाह: पंजाब के उपजाऊ दोआब मैदान।
-
मिट्टियाँ:
-
पंजाब मैदान में जलोढ़
-
उप-पर्वतीय क्षेत्रों में सवाना और फेरालिटिक
-
जलवायु और जल विज्ञान
-
नदी हिमपात पिघलने और मानसूनी वर्षा से पोषित होती है।
-
पाकिस्तान पंजाब (नारोवाल, शाहदरा, लाहौर) में मौसमी बाढ़ आम है।
-
जुलाई–सितंबर मानसून के दौरान अधिकतम प्रवाह।
आर्थिक और सांस्कृतिक महत्व
-
पंजाब के दोआब क्षेत्रों को सिंचाई प्रदान करती है।
-
जलविद्युत उत्पादन (चंबा, थीन परियोजनाएँ) का समर्थन करती है।
-
धार्मिक महत्व रखती है – विशेषकर करतारपुर साहिब और सिख विरासत।




