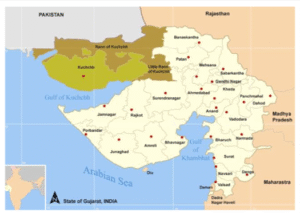
Overview of Rann of Kutch
-
A vast region of salt marshes that runs along the border between India and Pakistan
-
Primarily in Gujarat’s Kutch district, with a tiny area also extending into Pakistan’s Sindh province
-
It is separated into:
-
The greater part of the Great Rann of Kutch
-
Kutch’s Little Rann
-
Geographical Characteristics
-
Kutch’s Great Rann
-
-
Lies south of the Thar Desert and north of the Kutch Hills
-
In southern Pakistan, to the west, is the Indus River Delta
-
-
Kutch’s Little Rann
-
-
Southeast of the Great Rann
-
Reaches the Gulf of Kutch in the south
-
-
Weather
-
-
Summers are hot, with an average temperature of about 44°C and a maximum temperature of 50°C
-
Winters can be cold, with temperatures dropping to or below freezing
-
The area is the only sizable area of flooded grasslands in the realm of Indo-Malaya
-
Biodiversity and Ecology
-
Sustains a variety of ecosystems
-
-
Flooded grasslands
-
Mangroves
-
Desert vegetation
-
-
The Indian wild ass (Khur) lives in Little Rann
-
One of the eight biogeographic realms, the Indo-Malayan realm
-
-
Encompasses parts of East Asia as well as South and Southeast Asia
-
-
Gujarat is home to the Wild Ass Wildlife Sanctuary in Little Rann
-
-
India’s largest wildlife sanctuary
-
Historical Significance
-
The origins of Rann of Kutch can be traced to Neolithic settlement
-
Later, the Indus Valley Civilisation lived there
-
Empires that ruled the region include:
-
Gupta Empire
-
Maurya Empire
-
Geography of the Kutch Desert
-
Bordered to the west by the Arabian Sea
-
To the northeast by southwest Rajasthan and Sindh (Pakistan)
-
Characteristics of the recent geological era
-
-
Holocene sedimentation
-
-
Key Water Bodies
-
-
Kori Creek (in the west) connects to the Arabian Sea
-
Kutch Gulf (in the east)
-
-
Very near the ocean level
-
-
Contribute to seasonal level
-
कच्छ का रण:
कच्छ का रण: एक परिचय
-
यह नमक के दलदलों का एक विशाल क्षेत्र है जो भारत और पाकिस्तान की सीमा के साथ फैला हुआ है
-
मुख्य रूप से गुजरात के कच्छ जिले में स्थित है, जबकि इसका एक छोटा हिस्सा पाकिस्तान के सिंध प्रांत में भी फैला है
-
इसे दो भागों में बांटा गया है:
-
कच्छ का महान रण
-
कच्छ का छोटा रण
-
भौगोलिक विशेषताएं
-
कच्छ का महान रण
-
-
थार मरुस्थल के दक्षिण और कच्छ की पहाड़ियों के उत्तर में स्थित है
-
पश्चिम में, दक्षिणी पाकिस्तान में, सिंधु नदी का डेल्टा है
-
-
कच्छ का छोटा रण
-
-
महान रण के दक्षिण-पूर्व में स्थित है
-
दक्षिण में कच्छ की खाड़ी तक फैला हुआ है
-
-
मौसम
-
-
गर्मियों में तापमान औसतन लगभग 44°C रहता है और अधिकतम 50°C तक पहुंचता है
-
सर्दियों में तापमान शून्य डिग्री या उससे भी नीचे जा सकता है
-
यह क्षेत्र इंडो-मलाया जैविक क्षेत्र का एकमात्र बड़ा बाढ़ग्रस्त घास का मैदान है
-
जैव विविधता और पारिस्थितिकी
-
विभिन्न पारिस्थितिकी तंत्रों का समर्थन करता है
-
-
बाढ़ग्रस्त घास के मैदान
-
मैन्ग्रोव
-
रेगिस्तानी वनस्पति
-
-
भारतीय जंगली गधा (खुर) छोटा रण में पाया जाता है
-
यह इंडो-मलायन जैव-भौगोलिक क्षेत्र का हिस्सा है
-
-
जो पूर्वी एशिया और दक्षिण व दक्षिण-पूर्व एशिया के हिस्सों को शामिल करता है
-
-
गुजरात में स्थित है वाइल्ड ऐस वाइल्डलाइफ सैंक्चुअरी (Wild Ass Wildlife Sanctuary)
-
-
भारत का सबसे बड़ा वन्यजीव अभयारण्य
-
ऐतिहासिक महत्व
-
कच्छ के रण की उत्पत्ति नवपाषाण युग की बसावट से जुड़ी हुई है
-
बाद में यह क्षेत्र सिंधु घाटी सभ्यता का हिस्सा रहा
-
इस क्षेत्र पर शासन करने वाले साम्राज्य:
-
गुप्त साम्राज्य
-
मौर्य साम्राज्य
-
कच्छ के मरुस्थल का भूगोल
-
पश्चिम में अरब सागर से घिरा है
-
उत्तर-पूर्व में दक्षिण-पश्चिम राजस्थान और सिंध (पाकिस्तान) से सीमावर्ती
-
नवीनतम भूवैज्ञानिक युग की विशेषताएं
-
-
होलोसीन (Holocene) काल की तलछटी निर्माण प्रक्रिया
-
-
मुख्य जल निकाय
-
-
कोरी क्रीक (Kori Creek) (पश्चिम में) अरब सागर से जुड़ा है
-
कच्छ की खाड़ी (पूर्व में)
-
-
समुद्र तल के बहुत पास स्थित
-
-
जो मौसमी जल स्तर में योगदान देता है|
-




