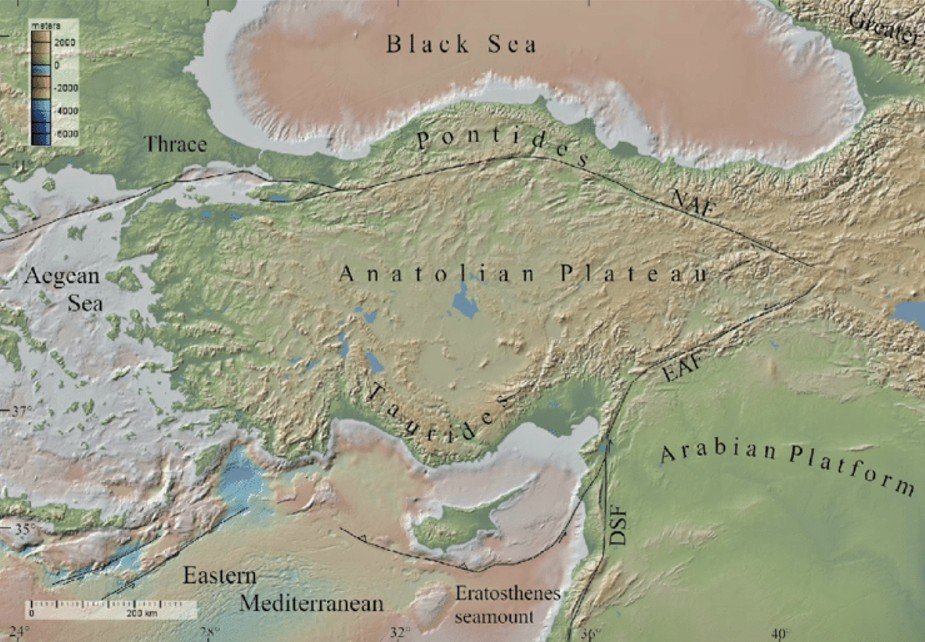
Anatolian Plateau is located in central Turkey, forming the Asian part of the country.
It lies between the Pontic Mountains in the north and the Taurus Mountains in the south.
The plateau has a continental climate, with hot summers and cold winters.
It is a region of high seismic activity due to the Anatolian Fault Zone.
The average elevation of the plateau is around 900 to 1,500 meters above sea level.
Major rivers like Kızılırmak and Sakarya originate from this upland region.
The plateau is largely semi-arid, supporting steppe vegetation and grazing.
Volcanic cones and extinct volcanoes such as Mount Erciyes are common.
The region includes Cappadocia, known for its unique rock formations and valleys.
The plateau is economically important for agriculture (especially cereals) and livestock.
It has a scattered population with major cities like Ankara, Turkey’s capital.
The plateau forms a key part of the Tectonic Anatolia Plate, bordered by Eurasian and Arabian plates.
The Anatolian Plateau is also referred to as Asia Minor in ancient geography.
It acts as a land bridge between Europe and Asia, influencing both tectonics and history.
The North Anatolian Fault (NAF) is a major strike-slip fault responsible for frequent earthquakes.
The plateau is a part of the Mediterranean belt, contributing to its high seismicity.
Loess and volcanic soils make certain areas fertile for dry farming despite the aridity.
The region played a central role in the Byzantine and Ottoman empires due to its strategic location.
अनातोलियन पठार:-
अनातोलियन पठार तुर्की के मध्य भाग में स्थित है, जो देश के एशियाई हिस्से में आता है।
यह पॉन्टिक पर्वत (उत्तर) और टॉरियस पर्वत (दक्षिण) के बीच फैला हुआ है।
इस क्षेत्र में महाद्वीपीय जलवायु पाई जाती है — गर्मी में गर्म और सर्दियों में अत्यधिक ठंड।
यह एक भूकंपीय रूप से सक्रिय क्षेत्र है क्योंकि यहाँ अनातोलियन फॉल्ट ज़ोन मौजूद है।
इसकी औसत ऊँचाई 900 से 1500 मीटर के बीच है और यह समुद्र तल से ऊपर है।
किज़िलिर्मक और साकार्या जैसी प्रमुख नदियाँ इसी पठारी क्षेत्र से निकलती हैं।
यह इलाका अधिकांशतः अर्ध-शुष्क है, जहाँ घासभूमि और पशुपालन प्रचलित हैं।
यहाँ कई ज्वालामुखी शंकु और निष्क्रिय ज्वालामुखी (जैसे माउंट एरसीयस) स्थित हैं।
यह क्षेत्र कैप्पाडोसिया के लिए प्रसिद्ध है, जहाँ अद्वितीय चट्टानी संरचनाएँ और घाटियाँ मिलती हैं।
यहाँ का कृषि क्षेत्र, विशेषतः अनाज उत्पादन और पशुपालन, आर्थिक रूप से महत्त्वपूर्ण है।
जनसंख्या छिटपुट रूप से बसी है, और अंकारा (तुर्की की राजधानी) इसी क्षेत्र में है।
यह पठार अनातोलियन टेक्टोनिक प्लेट का हिस्सा है, जिसे यूरेशियन व अरब प्लेटें घेरे हुए हैं।
अनातोलियन पठार को प्राचीन भूगोल में एशिया माइनर भी कहा जाता था।
यह यूरोप और एशिया के बीच एक भौगोलिक पुल की तरह कार्य करता है।
नॉर्थ अनातोलियन फॉल्ट एक प्रमुख स्ट्राइक-स्लिप फॉल्ट है जिससे भूकंप आते हैं।
यह भूमध्यसागरीय भूकंपीय बेल्ट का हिस्सा है, जिससे इसकी भूकंपीयता अधिक है।
यहाँ की मिट्टी लोस और ज्वालामुखी प्रकार की होती है, जिससे कुछ क्षेत्र सूखी कृषि के लिए उपयुक्त होते हैं।
इस क्षेत्र का इतिहास में महत्व रहा है, क्योंकि यह बाइज़ेंटाइन और ओटोमन साम्राज्यों का केंद्र रहा है।