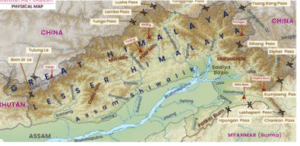
Arunachal Pradesh:
Location
-
India’s easternmost state
-
Coordinates:
-
Latitude: 26° 37′ N to 29° 28′ N
-
Longitude: 91° 32′ E to 97° 26′ E
-
-
81,424 square kilometres in total
-
Itanagar is the capital
-
Formerly known as the North-East Frontier Agency (NEFA)
-
In 1972, the Union Territory was established
-
Statehood was attained in 1987
Adjacent Areas
-
Assam in the south
-
Southeast: Nagaland
-
Myanmar (Burma) in the east
-
Bhutan in the west
-
North: China’s Tibet region
Terrain and Topography
-
A section of the Eastern Himalayas
-
Most of Lohit, Changlang, and Tirap districts are covered by the Greater Himalayan ranges
-
Patkai hill ranges cover the remaining areas
-
Comprises mountainous highlands that reach the plains of Assam
-
Resides entirely on the Eurasian plate
Highlights of Culture and Demographics
-
Inhabited by tribes of Mongols
-
The majority of tribes practise animism
-
Meaning of the name: Arunachal Pradesh means “land” in Sanskrit
-
Of the mountains illuminated by dawn
-
-
Because of its eastern location, it is referred to as the “land of the rising sun”
Significant Peaks
-
Nyegi Kangsang
-
Kangto
-
Gorichen Peak
-
Main Gorichen Peak in the East
-
Significant Tribes and Hill Ranges
Dafla Hills
-
Situated north of Tezpur in the western region of Arunachal Pradesh
Abor Range
-
Forms its eastern boundary
Abor Hills
-
Inhabited by the Dafla tribe
-
Situated in the southern region
-
Located close to the China border in the far northeast
-
Drained by the Brahmaputra tributary, the Dibang River
-
The Abor tribe resides there
Mishmi Hills
-
Situated in the Great Himalayas’ eastern, southward extension
-
Touches the Chinese border
Patkai Bum Hills
-
Situated on the eastern and northern borders, particularly close to Myanmar (Burma)
-
Inhabited by the Mishmi tribe
-
Form a natural barrier between India and Burma in Changlang and Tirap districts
-
Name origin: “Patkai” means “to cut chicken” in Tai-Ahom language
-
Known for:
-
Conical peaks
-
Steep slopes
-
Deep valleys
-
-
Home to Chakma and other ethnic groups
-
Rich in biodiversity and cultural landmarks like temples and monasteries
अरुणाचल प्रदेश:
अरुणाचल प्रदेश: एक व्यापक भौगोलिक अवलोकन
स्थान
-
भारत का सबसे पूर्वी राज्य
-
निर्देशांक:
-
अक्षांश: 26° 37′ N से 29° 28′ N
-
देशांतर: 91° 32′ E से 97° 26′ E
-
-
कुल क्षेत्रफल: 81,424 वर्ग किलोमीटर
-
ईटानगर राजधानी है
-
पहले इसे नॉर्थ-ईस्ट फ्रंटियर एजेंसी (NEFA) कहा जाता था
-
1972 में केंद्र शासित प्रदेश के रूप में स्थापित किया गया
-
1987 में राज्य का दर्जा प्राप्त हुआ
समीपवर्ती क्षेत्र
-
दक्षिण में असम
-
दक्षिण-पूर्व में नागालैंड
-
पूर्व में म्यांमार (बर्मा)
-
पश्चिम में भूटान
-
उत्तर में चीन का तिब्बत क्षेत्र
भूमि-रूप और स्थलाकृति
-
पूर्वी हिमालय का एक भाग
-
लोहित, चांगलांग और तिरप जिलों के अधिकांश भाग ग्रेटर हिमालय श्रेणियों से आच्छादित
-
शेष भाग पतकै पर्वतमाला से ढका हुआ
-
यह क्षेत्र असम के मैदानी भागों तक फैले हुए पर्वतीय उच्च भूमि से युक्त है
-
पूरी तरह यूरेशियन प्लेट पर स्थित है
संस्कृति और जनसांख्यिकी की विशेषताएं
-
मंगोल जनजातियों द्वारा बसा हुआ
-
अधिकांश जनजातियाँ एनीमिज़्म (प्रकृति पूजा) का पालन करती हैं
-
नाम का अर्थ: अरुणाचल प्रदेश का संस्कृत में अर्थ “भूमि”
-
जो सुबह की रोशनी से प्रकाशित पहाड़ियों की भूमि है
-
-
पूर्व में स्थित होने के कारण इसे “उगते सूरज की भूमि” कहा जाता है
प्रमुख पर्वत शिखर
-
न्येगी कांगसांग
-
कांगटो
-
गोरिचेन पीक
-
पूर्व में मुख्य गोरिचेन पीक
-
प्रमुख जनजातियाँ और पर्वत श्रृंखलाएँ
दाफ़ला हिल्स
-
पश्चिमी अरुणाचल प्रदेश में तेज़पुर के उत्तर में स्थित
अबोर रेंज
-
इसका पूर्वी सीमा बनाती है
अबोर हिल्स
-
दाफ़ला जनजाति द्वारा आबाद
-
दक्षिणी क्षेत्र में स्थित
-
दूर उत्तर-पूर्व में चीन की सीमा के निकट स्थित
-
ब्रह्मपुत्र की सहायक नदी, दीबांग नदी द्वारा बहाया जाता है
-
अबोर जनजाति यहाँ निवास करती है
मिश्मी हिल्स
-
ग्रेट हिमालय की पूर्वी, दक्षिणवर्ती विस्तार में स्थित
-
चीन की सीमा को छूती है
पतकै बुम हिल्स
-
पूर्वी और उत्तरी सीमा पर स्थित, विशेष रूप से म्यांमार (बर्मा) के पास
-
मिश्मी जनजाति द्वारा आबाद
-
चांगलांग और तिरप जिलों में भारत और बर्मा के बीच एक प्राकृतिक अवरोध बनाती हैं
-
नाम की उत्पत्ति: “पतकै” का ताई-अहोम भाषा में अर्थ “मुर्गी काटना”
-
प्रसिद्ध हैं:
-
शंक्वाकार चोटियों
-
खड़ी ढलानों
-
गहरी घाटियों के लिए
-
-
चकमा और अन्य जातीय समूहों का निवास स्थान
-
जैव विविधता और सांस्कृतिक स्थलों जैसे मंदिरों और मठों से समृद्ध




