Basics
-
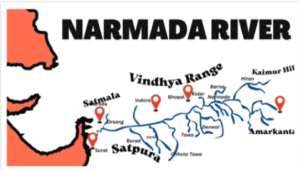
The Narmada River is the biggest river in the Indian peninsula that flows west.
-
It passes through a rift valley to the west between:
-
Range of Vindhya (to the north)
-
Range of Satpura (to the south)
-
Origin and Path
-
Source: Madhya Pradesh’s Maikala Range, close to Amarkantak
-
Source elevation: approximately 1057 meters
-
Length: roughly 1,310 kilometres (from the Gulf of Khambhat to Amarkantak)
-
Estuary: Empties into the Arabian Sea’s Gulf of Khambhat
Basin for Drainage
-
Covered area: approximately one lakh square kilometres
-
Covered states:
-
Madhya Pradesh
-
Gujarat
-
Maharashtra
-
Chhattisgarh
-
-
The basin’s boundaries:
-
North: Vindhyas
-
East: The Maikala range
-
South: Satpura range
-
West: Arabian Sea
-
Geographical Characteristics
-
Hilly terrain in the upper basin
-
Broad and fertile, the middle and lower reaches are ideal for farming
-
Jabalpur is an important urban centre
Waterfalls and Famous Locations
-
The river close to Jabalpur descends 15 meters into a ravine to form Dhuan Dhar (Cloud of Mist) Falls
-
The gorge is known as Marble Rocks and is composed of marble
-
Other noteworthy waterfalls include:
-
Dardi and Mandhar: Every 12 m
-
Sahasradhara Falls: An 8-meter waterfall close to Maheshwar
-
Navigation and Estuaries
-
The estuary contains a number of islands
-
The largest island is Aliabet
-
-
Up to 112 kilometres from its mouth, the river is navigable
Narmada Tributaries
-
General Features:
-
A narrow valley with steep hills is traversed by the river
-
Has a small number of tributaries, particularly on the right bank
-
-
Tributaries on the right bank:
-
Hiran (notable as the only prominent one)
-
Barna
-
Orsang
-
The northern slopes of the Satpura Range are the source of the Kolar
-
-
Left Bank Tributaries:
-
Join the Narmada at different places
-
Large-scale Hydropower Projects in Narmada Basin
-
Indira Sagar Project
-
Sardar Sarovar Project
-
Omkareshwar Dam
-
Bargi Dam
-
Maheshwar Project
नर्मदा नदी :
मूल विवरण
-
नर्मदा नदी भारतीय प्रायद्वीप की सबसे बड़ी पश्चिम की ओर बहने वाली नदी है।
-
यह एक दरार घाटी से होकर पश्चिम की ओर बहती है, जो स्थित है:
-
विन्ध्य पर्वत श्रृंखला (उत्तर में)
-
सतपुड़ा पर्वत श्रृंखला (दक्षिण में)
-
उद्गम और मार्ग
-
स्रोत: मध्य प्रदेश के मैकल श्रेणी में, अमरकंटक के पास
-
स्रोत की ऊँचाई: लगभग 1057 मीटर
-
लंबाई: लगभग 1,310 किलोमीटर (अमरकंटक से खंभात की खाड़ी तक)
-
मुहाना: अरब सागर की खंभात की खाड़ी में गिरती है
जल निकासी बेसिन
-
कवर क्षेत्र: लगभग एक लाख वर्ग किलोमीटर
-
कवर राज्य:
-
मध्य प्रदेश
-
गुजरात
-
महाराष्ट्र
-
छत्तीसगढ़
-
-
बेसिन की सीमाएँ:
-
उत्तर: विन्ध्य श्रृंखला
-
पूर्व: मैकल श्रेणी
-
दक्षिण: सतपुड़ा श्रृंखला
-
पश्चिम: अरब सागर
-
भौगोलिक विशेषताएँ
-
ऊपरी बेसिन में पहाड़ी इलाका
-
मध्य और निचले भाग चौड़े और उपजाऊ हैं, जो खेती के लिए उपयुक्त हैं
-
जबलपुर एक प्रमुख नगरीय केंद्र है
झरने और प्रसिद्ध स्थान
-
नदी जबलपुर के पास 15 मीटर की ऊँचाई से एक खाई में गिरती है, जिससे धुआँधार जलप्रपात (मिस्ट का बादल) बनता है
-
यह खाई संगमरमर से बनी है और इसे मार्बल रॉक्स कहा जाता है
-
अन्य प्रमुख झरनों में शामिल हैं:
-
दरदी और मंधार: प्रत्येक 12 मीटर
-
सहस्त्रधारा जलप्रपात: महेश्वर के पास स्थित 8 मीटर का जलप्रपात
-
नेविगेशन और मुहाने
-
मुहाने में कई द्वीप हैं
-
सबसे बड़ा द्वीप अलीआबेट है
-
-
अपने मुहाने से 112 किलोमीटर तक यह नदी नौवहन योग्य है
नर्मदा की सहायक नदियाँ
-
सामान्य विशेषताएँ:
-
नदी एक संकरी घाटी से गुजरती है, जिसके चारों ओर खड़ी पहाड़ियाँ हैं
-
विशेषकर दाहिने किनारे पर बहुत कम सहायक नदियाँ हैं
-
-
दाहिने किनारे की सहायक नदियाँ:
-
हिरण (केवल प्रमुख सहायक नदी के रूप में जानी जाती है)
-
बर्ना
-
ओरसांग
-
सतपुड़ा श्रृंखला की उत्तरी ढलानों से निकलने वाली कोलार
-
-
बाएँ किनारे की सहायक नदियाँ:
-
विभिन्न स्थानों पर नर्मदा से मिलती हैं
-
नर्मदा बेसिन में बड़े पैमाने की जलविद्युत परियोजनाएँ
-
इंदिरा सागर परियोजना
-
सरदार सरोवर परियोजना
-
ओंकारेश्वर डैम
-
बरगी डैम
-
महेश्वर परियोजना




