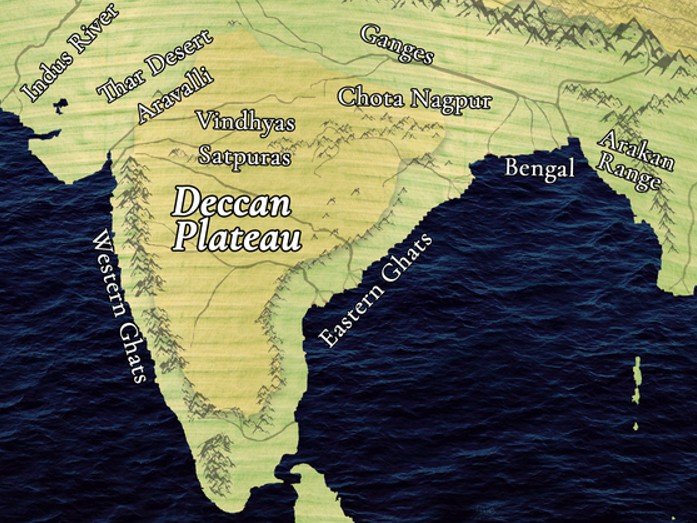
The Eastern Plateau lies to the east of Central Highlands and south of the Chotanagpur Plateau.
It is part of the Peninsular Plateau and consists mainly of Precambrian rocks like granite and gneiss.
This region covers parts of Jharkhand, Odisha, Chhattisgarh, West Bengal, and Andhra Pradesh.
The Chotanagpur Plateau is a major component of the Eastern Plateau with undulating highlands.
Major rivers include Subarnarekha, Damodar, Brahmani, Mahanadi, and Indravati.
These rivers mostly flow west to east and drain into the Bay of Bengal.
The area receives around 100–150 cm rainfall, mainly during the southwest monsoon.
The climate is tropical wet and dry, with hot summers and mild winters.
Soils are mainly laterite and red, acidic and low in fertility.
Natural vegetation is tropical deciduous, dominated by sal and teak trees.
The region is rich in coal and iron ore, especially in Jharia and Keonjhar.
Important coalfields are Jharia, Bokaro, and Raniganj in the Damodar Valley.
Major industries include iron and steel, and thermal power plants.
Agricultural practices are largely subsistence based, with rice and millets as main crops.
Shifting cultivation like podu farming is practiced in tribal regions.
Tribal groups like Santhals and Gonds depend on forest-based livelihoods.
The terrain is rugged and dissected, marked by low hills and narrow valleys.
Cities like Ranchi and Rourkela are major industrial hubs in the region.
Environmental concerns include mining pollution and large-scale deforestation.
Unregulated mining has led to land degradation and tribal displacement.
पूर्वी पठार:-
पूर्वी पठार भारत के मध्य उच्चभूमि के पूर्व में और छोटानागपुर पठार के दक्षिण में स्थित है।
यह प्रायद्वीपीय पठार का हिस्सा है और मुख्य रूप से प्राक्कैम्ब्रियन चट्टानों जैसे ग्रेनाइट और ग्नीस से बना है।
यह क्षेत्र झारखंड, ओडिशा, छत्तीसगढ़, पश्चिम बंगाल और आंध्र प्रदेश के कुछ हिस्सों में फैला है।
छोटानागपुर पठार पूर्वी पठार का एक प्रमुख भाग है और इसमें तरंगित उच्चभूमियाँ पाई जाती हैं।
प्रमुख नदियाँ हैं स्वर्णरेखा, दामोदर, ब्राह्मणी, महानदी और इंद्रावती।
ये नदियाँ प्रायः पश्चिम से पूर्व की ओर बहती हैं और बंगाल की खाड़ी में गिरती हैं।
इस क्षेत्र में औसतन 100–150 सेमी वर्षा होती है, जो मुख्यतः दक्षिण-पश्चिम मानसून से आती है।
यहाँ की जलवायु उष्णकटिबंधीय आद्र्र एवं शुष्क है, जिसमें गर्मी तीव्र और सर्दी मध्यम होती है।
मिट्टियाँ मुख्यतः लेटराइट एवं लाल होती हैं और अम्लीय तथा कम उपजाऊ होती हैं।
प्राकृतिक वनस्पति में उष्णकटिबंधीय पर्णपाती वन, विशेष रूप से साल और सागौन प्रमुख हैं।
यह क्षेत्र कोयला और लौह अयस्क जैसे खनिजों से समृद्ध है, विशेष रूप से झारिया और क्योंझर में।
प्रमुख कोयला क्षेत्र हैं झारिया, बोकारो, और दामोदर घाटी में रानीगंज।
प्रमुख उद्योगों में लौह एवं इस्पात, तथा थर्मल पॉवर प्लांट्स शामिल हैं।
कृषि प्रणाली मुख्यतः आजीविकात्मक खेती है, जिसमें चावल और बाजरा प्रमुख फसलें हैं।
आदिवासी क्षेत्रों में झूम खेती जैसे पोड़ू कृषि प्रचलित है।
संथाल और गोंड जैसे जनजातीय समूह वन संसाधनों पर निर्भर हैं।
यह भू-आकृति अवकाशयुक्त एवं बीहड़ है, जिसमें निम्न पर्वत श्रृंखलाएं और संकरी घाटियाँ पाई जाती हैं।
रांची और राउरकेला जैसे शहर इस क्षेत्र के प्रमुख औद्योगिक केंद्र हैं।
पर्यावरणीय समस्याओं में खनन से प्रदूषण और वृक्षों की कटाई प्रमुख हैं।
अनियंत्रित खनन के कारण भूमि क्षरण और जनजातीय विस्थापन हुआ है।