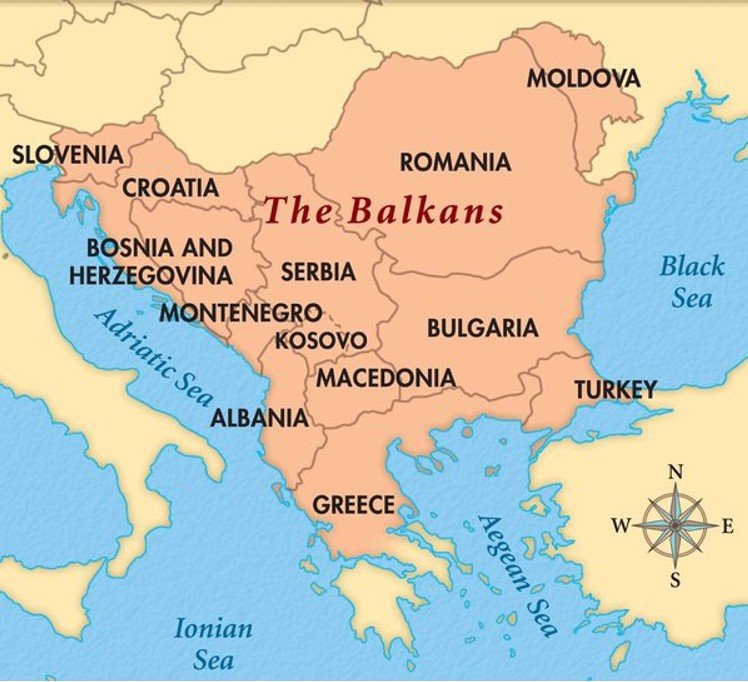
The Balkan Plateau lies in southeastern Europe and forms the core of the Balkan Peninsula.
It spans across Serbia, Kosovo, Montenegro, parts of North Macedonia, Albania, and western Bulgaria.
The plateau is a section of the Alpine–Himalayan orogenic belt, created by the African–Eurasian plate collision.
It is bordered by the Dinaric Alps in the west and Rhodopes Mountains in the east.
It consists mainly of limestone and dolomite rocks, with notable karst topography.
Terrain is rugged and dissected, with river valleys and basin-like depressions.
The Morava River and Vardar River cut through the plateau and act as natural trade corridors.
Average elevation ranges from 500 to 1,200 metres, with several isolated highlands.
It has rich mineral resources, especially lead, zinc, iron ore, and copper.
The plateau has areas of coal mining and non-ferrous metallurgy industries.
Climate varies from continental in inland parts to Mediterranean in coastal extensions.
Inland areas have cold winters and warm summers, while coasts are mild and rainy.
Vegetation includes oak, pine, and beech forests, with patches of shrubs and pastures.
Sheep and goat rearing is common, especially in hilly and karstic zones.
Agriculture is practiced in river valleys and plains, mostly wheat, maize, grapes, and olives.
The region is seismically active and prone to earthquakes due to tectonic collisions.
It serves as a transition zone between Central Europe and Western Asia.
The plateau is ethnically diverse, including Slavs, Albanians, Greeks, and Turks.
The term “Balkan” comes from the Turkish word meaning “a chain of wooded mountains”.
The region has historically faced ethnic tensions, including the Balkan Wars (1912–13).
World War I began in this region after the assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand in Sarajevo.
It was part of the former Yugoslavia, which disintegrated into seven independent countries.
Modern Balkan states are critical to EU expansion and NATO’s southeastern flank.
The region features transport bottlenecks, but also major routes like Pan-European Corridor X.
The Balkan Plateau acts as a cultural and physical crossroad between Europe and Asia.
बाल्कन पठार:-
बाल्कन पठार दक्षिण-पूर्वी यूरोप में स्थित है और बाल्कन प्रायद्वीप का मुख्य भाग है।
यह सर्बिया, कोसोवो, मोंटेनेग्रो, के साथ-साथ उत्तरी मैसेडोनिया, अल्बानिया और पश्चिमी बुल्गारिया तक फैला है।
यह ऐल्पाइन–हिमालय पर्वत श्रृंखला का भाग है, जो अफ्रीकी व यूरेशियन प्लेट के टकराव से बना।
इसके पश्चिम में डायनारिक एल्प्स और पूर्व में रोडोपे पर्वत श्रृंखला स्थित हैं।
इसकी चट्टानें मुख्यतः चूना पत्थर और डोलोमाइट से बनी हैं, और इसमें कार्स्ट स्थलाकृति पाई जाती है।
इसकी भूमि ऊबड़-खाबड़ और विखंडित है, जिसमें नदी घाटियाँ और निचले गर्त पाए जाते हैं।
मोरावा नदी और वारदार नदी इस पठार से गुजरती हैं और प्राकृतिक व्यापार मार्ग बनाती हैं।
इसकी औसत ऊँचाई 500 से 1,200 मीटर है, और इसमें पृथक उच्चभूमियाँ पाई जाती हैं।
क्षेत्र में सीसा, जस्ता, तांबा, और लौह अयस्क जैसे खनिज संसाधन प्रचुर मात्रा में हैं।
यहाँ कोयला खनन और अलौह धातु उद्योग भी विकसित हैं।
इसका जलवायु महाद्वीपीय से लेकर भूमध्यसागरीय तक फैला है।
भीतरी क्षेत्र ठंडी सर्दी और गर्म गर्मी का अनुभव करते हैं, जबकि तटीय क्षेत्र मिलनसार और आर्द्र होते हैं।
वनस्पति में ओक, पाइन और बीच के जंगल, साथ में झाड़ियों और घास के मैदान शामिल हैं।
भेड़ और बकरी पालन विशेषकर पहाड़ी व कार्स्ट क्षेत्रों में आम है।
नदी घाटियों और समतल भूभाग में कृषि होती है, मुख्य फसलें हैं गेहूं, मक्का, अंगूर और जैतून।
यह क्षेत्र भूकंपीय रूप से सक्रिय है और भूकंपों के लिए संवेदनशील है।
यह केंद्रीय यूरोप और पश्चिमी एशिया के बीच एक संक्रमण क्षेत्र है।
यहाँ स्लाव, अल्बानियन, ग्रीक और तुर्क जैसे विविध जातीय समूह रहते हैं।
बाल्कन शब्द की उत्पत्ति तुर्की भाषा से हुई है, जिसका अर्थ है “वनाच्छादित पर्वतों की श्रृंखला”।
यह क्षेत्र ऐतिहासिक रूप से जातीय संघर्षों से ग्रस्त रहा, जैसे कि बाल्कन युद्ध (1912–13)।
प्रथम विश्व युद्ध की शुरुआत यहीं से हुई, जब आर्चड्यूक फ्रांज फर्डिनेंड की सारायेवो में हत्या हुई।
यह कभी यूगोस्लाविया का हिस्सा था, जिसका विघटन होकर 7 स्वतंत्र देश बने।
वर्तमान बाल्कन राष्ट्र यूरोपीय संघ के विस्तार और नाटो की दक्षिण-पूर्वी रणनीति में महत्त्वपूर्ण हैं।
यह क्षेत्र परिवहन अवरोधों से ग्रस्त है, लेकिन पैन-यूरोपीय कॉरिडोर X जैसे प्रमुख मार्ग भी हैं।
बाल्कन पठार एक सांस्कृतिक और भौगोलिक संगम क्षेत्र है, जो यूरोप और एशिया को जोड़ता है।