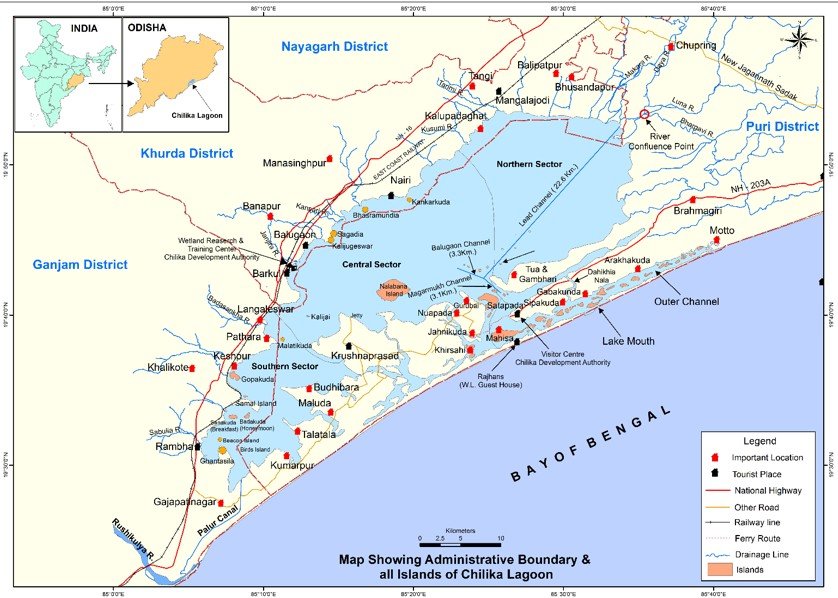
Chilika Lake is the largest brackish water lagoon in Asia and the second-largest in the world.
It is located along the east coast of India, spanning the Puri, Khurda, and Ganjam districts of Odisha.
The lake is connected to the Bay of Bengal via a narrow mouth near Satapada.
It was the first Indian wetland to be designated as a Ramsar Site under the Ramsar Convention in 1981.
Chilika supports over 160 species of birds, including migratory birds from Siberia, Iran, and Central Asia.
The lake is home to the vulnerable Irrawaddy dolphins, found mainly in the Satapada area.
It hosts a rich variety of aquatic flora and fauna, including crustaceans, mollusks, and fish species.
Nalabana Island, located within Chilika, is a bird sanctuary notified under the Wildlife Protection Act, 1972.
The lake supports the livelihoods of over 200,000 fishermen living in and around its basin.
It is a major source of fishery resources, especially prawns, crabs, and mackerel.
Chilika is a popular ecotourism destination, known for boating, birdwatching, and dolphin sightings.
Chilika was included in the Montreux Record in 1993 due to its degraded ecological condition.
After successful restoration by the Chilika Development Authority (CDA), it was removed from Montreux Record in 2002.
Restoration efforts included opening a new mouth to the sea, improving salinity levels and biodiversity.
The CDA was established by the Government of Odisha for lake conservation and management.
Chilika Lake has been declared an Important Bird Area (IBA) by BirdLife International.
It plays a crucial role in climate resilience and disaster mitigation in coastal Odisha.
Satellite monitoring and AI-based tracking are being used to study the movement of dolphins and migratory birds.
Key Facts (in One-Liners):
Location: Odisha
Type: Brackish water lagoon
Connected to: Bay of Bengal
Famous for: Irrawaddy Dolphins
Island Sanctuary: Nalabana
Protected Under: Ramsar Convention, Wildlife Protection Act
Restoration Body: Chilika Development Authority
Removed from Montreux Record: 2002
चिल्का झील:-
चिल्का झील एशिया की सबसे बड़ी खारे पानी की लैगून है।
यह भारत के पूर्वी तट पर स्थित है और पुरी, खुर्दा व गंजम ज़िलों में फैली है।
यह झील बंगाल की खाड़ी से सतपाड़ा के पास एक संकीर्ण द्वार से जुड़ती है।
यह भारत की पहली आर्द्रभूमि थी जिसे 1981 में रामसर स्थल के रूप में मान्यता मिली।
चिल्का में 160 से अधिक पक्षी प्रजातियाँ पाई जाती हैं, जिनमें साइबेरिया, ईरान व मध्य एशिया से आने वाले प्रवासी पक्षी भी शामिल हैं।
यह झील संवेदनशील इरावडी डॉल्फ़िन का निवास है, जो मुख्यतः सतपाड़ा क्षेत्र में पाई जाती हैं।
इसमें जलजीवों और वनस्पतियों की समृद्ध विविधता है, जैसे क्रस्टेशियन्स, मोलस्क और मछलियाँ।
नलाबाना द्वीप, जो झील के भीतर स्थित है, को वन्यजीव संरक्षण अधिनियम, 1972 के अंतर्गत पक्षी अभयारण्य घोषित किया गया है।
यह झील 2 लाख से अधिक मछुआरों की आजिविका का स्रोत है।
यह मत्स्य संसाधनों का मुख्य स्रोत है, विशेषकर झींगे, केकड़े और मैकरल।
चिल्का एक प्रसिद्ध ईको-टूरिज़्म स्थल है, जहाँ बोटिंग, पक्षी अवलोकन और डॉल्फ़िन दर्शन होते हैं।
चिल्का को 1993 में मोंट्रेक्स रिकॉर्ड में शामिल किया गया था क्योंकि इसकी पारिस्थितिकी बिगड़ रही थी।
चिल्का विकास प्राधिकरण (CDA) के सफल प्रयासों के बाद इसे 2002 में मोंट्रेक्स रिकॉर्ड से हटा दिया गया।
पुनर्स्थापन में समुद्र से नया द्वार खोला गया, जिससे लवणता व जैव विविधता में सुधार हुआ।
CDA की स्थापना ओडिशा सरकार द्वारा झील संरक्षण व प्रबंधन हेतु की गई।
चिल्का को बर्डलाइफ इंटरनेशनल द्वारा महत्वपूर्ण पक्षी क्षेत्र (IBA) घोषित किया गया है।
यह जलवायु लचीलापन और आपदा न्यूनीकरण में अहम भूमिका निभाती है।
यहाँ उपग्रह निगरानी व AI आधारित तकनीक से डॉल्फिन और प्रवासी पक्षियों की गतिविधियाँ ट्रैक की जाती हैं।
प्रमुख तथ्य (एक-पंक्तीय रूप में):
स्थान: ओडिशा
प्रकार: खारे पानी की लैगून
जुड़ी हुई: बंगाल की खाड़ी से
प्रसिद्ध: इरावडी डॉल्फ़िन के लिए
द्वीप अभयारण्य: नलाबाना
संरक्षित: रामसर कन्वेंशन, वन्यजीव संरक्षण अधिनियम
पुनर्स्थापन निकाय: चिल्का विकास प्राधिकरण
हटाई गई: 2002 में मोंट्रेक्स रिकॉर्ड से